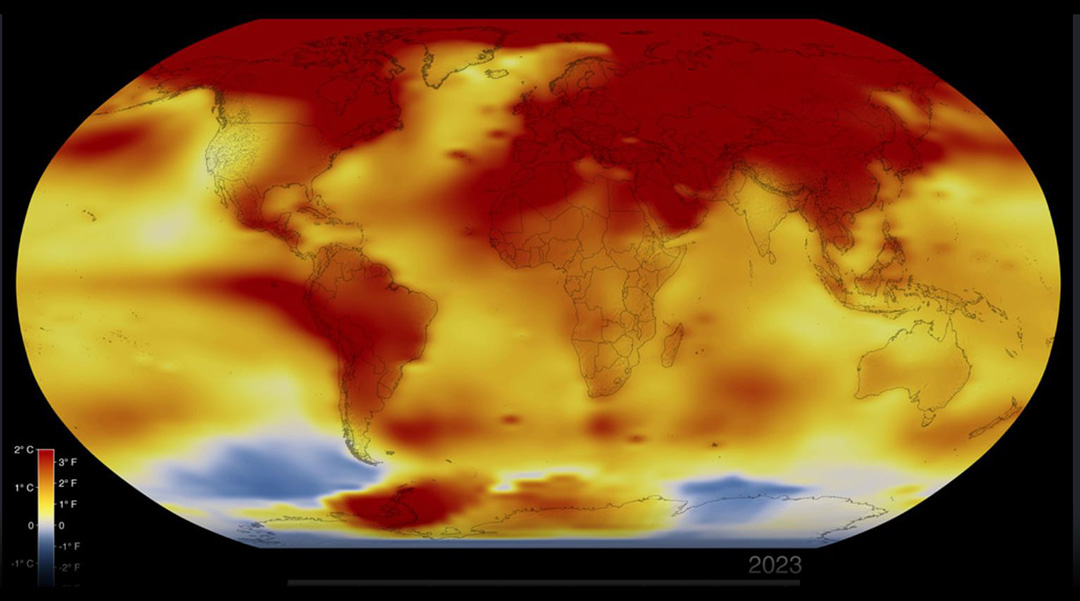
In 2023, Earth experienced its warmest average surface temperatures on record, surpassing the previous high set in 2016. This troubling development is highlighted in the second annual Indicators of Global Climate Change report, led by the University of Leeds. The report underscores a significant rise in human-induced global warming, with temperatures increasing by 1.19 degrees Celsius from 2014 to 2023. This marks a slight acceleration from the 1.14 degrees Celsius increase observed between 2013 and 2022, as documented in the initial report.
Piers Forster, director of the Priestley Centre for Climate Futures at the University of Leeds and coordinator of the report, expressed deep concern over these findings. He pointed out that despite efforts to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, human activities continue to drive a relentless upward trend in global temperatures. Forster emphasized the report’s comprehensive approach, which integrates various global datasets to analyze the factors contributing to human-induced global warming, including emissions trends, atmospheric concentrations, ocean heat absorption, and surface temperature trends.
In its assessment of 2023, the report identified a total warming of 1.4 degrees Celsius. Of this warming, 1.3 degrees Celsius was directly attributed to human activities, with the remainder influenced by natural factors such as El Niño conditions, which also played a role in the year’s record temperatures.
Forster highlighted the alarming pace at which human-driven warming is escalating, noting an unprecedented rate of 0.3 degrees Celsius per decade. He underscored the critical connection between this accelerated warming and elevated levels of greenhouse gas emissions, stressing the urgent need for enhanced global climate action.
The report’s broader objective is to track long-term trends in global warming, providing essential insights to inform policy decisions and strategies aimed at mitigating climate change. By illuminating the complex dynamics at play, the report serves as a vital tool in addressing the escalating environmental challenges facing our planet.
Implications for greenhouse gas emissions
Human-driven climate change is predominantly caused by the release of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, through the combustion of fossil fuels. These emissions constitute approximately 70% of all greenhouse gas emissions, making them the primary driver of global warming. However, other sources such as cement production, agriculture, deforestation, and reductions in sulfur emissions also contribute to the overall warming of the planet.
In 2020, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) outlined that to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2030, the allowable carbon dioxide emission budget was estimated to be between 300 to 900 billion tons, with a median estimate of 500 billion tons over the decade leading to 2030. Fast forward to early 2024, and it was projected that only 100 to 450 billion tons of this carbon budget remained, with a central estimate of 200 billion tons left.
The recent second annual Indicators of Global Climate Change report highlighted that merely 200 billion tons of the carbon dioxide budget set in 2020 by the IPCC remains available. This remaining budget equates to approximately five years’ worth of current emissions at the rate of 53 billion tons of carbon dioxide per year from 2014 to 2023. It’s important to note that improvements in air quality, while beneficial in reducing atmospheric particles, have inadvertently contributed to global warming by lowering the Earth’s albedo—the amount of solar energy reflected back into space.
Overall, the persistent high levels of greenhouse gas emissions have been a significant factor in the accelerated rate of global warming observed over the past decade. As efforts continue to mitigate these emissions and address their various sources, the challenge remains urgent to stay within the limits necessary to avoid the most severe impacts of climate change.
Are human actions sufficient to address global warming?
Efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions are evident, but the question remains: are humanity’s actions enough to effectively combat global warming? Significant strides have been made, such as the adoption of renewable energy over fossil fuels and the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and heat pumps. These shifts have contributed to a global slowdown in the growth of greenhouse gas emissions, which, while not yet back to pre-pandemic levels, show promising signs of stabilization.
According to experts like Forster, rapidly reducing emissions towards net zero is crucial to limiting the severity of rising global warming. They emphasize that halving emissions by 2030 could also halve the rate of temperature rise. However, achieving long-term climate stability requires a complete reduction of emissions to zero.
Despite pledges from many countries to take action, there is concern that current efforts fall short of what is necessary. Recently, the UN Secretary-General highlighted findings from the second annual Indicators of Global Climate Change report to urge countries to intensify their commitments. This report is expected to influence updated climate plans, known as Nationally Determined Contributions, which all nations are slated to submit to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) by 2025.
Forster underscores the urgency for countries worldwide to earnestly pursue their net zero goals, stressing that the costs of inaction regarding rising global warming far outweigh those of taking decisive action. As the world grapples with the imperative to mitigate emissions and adapt to climate impacts, the need for coordinated, ambitious efforts remains paramount in addressing the escalating challenges posed by global warming.
- ONLINE NEWS Lea, R. (2024, June 18). The rate of human-driven global warming is at a record high. Advanced Science News. [Advanced Science News]
- WEBSITE NASA Science. (n.d.). What is climate change?. NASA Science. [NASA Science]
- ONLINE NEWS BBC News. (2024, February 8). What is climate change? A really simple guide. BBC News. [BBC News]
APA 7: TWs Editor. (2024, June 18). Rising Global Warming Crisis: What the Human Surge?!. PerEXP Teamworks. [Online News Link]
















